Technical Support
Intended Use
Beet necrotic yellow vein virus (BNYVV) is the causal agent of Rhizomania, which is one of the most serious diseases
of sugarbeet and can greatly reduce sugar yield. The disease effects Beta vulgaris subsp.; sugar beet, fodder beet, red
beet, mangolds, sea kale beet, Swiss Chard and Spinacea oleracea (spinach). Symptoms of the disease are varied and
include root bearding, root stunting, chlorosis of leaves, yellow veining and necrosis of leaf veins.
Beet necrotic yellow vein virus Pocket Diagnostic is a rapid diagnostic test designed to be used in the field, nursery or
glasshouse. The test can be performed within minutes by operators with little or no training. Samples for testing can
be taken from any part of the plant, at any stage during the production cycle. Pocket Diagnostic test results form an
important part of sound decision making in routine screening or disease control situations.
Beet necrotic yellow vein virus Test Kit Contents:
· Test device (x4)
· Bottle of extraction buffer (including ball bearing) (x4)
· Pipette (x4)
· Instructions for Use
Quality Standards
Pocket Diagnostic tests are manufactured in environmentally-controlled facilities by Forsite Diagnostics Ltd, trading
as Abingdon Health, following procedures which meet ISO9001 quality standards and where possible validated to the
European and Mediterranean Plant Protection Organisation (EPPO) standards.
Storage and Shelf life
Pocket Diagnostic Kits should be stored at room temperature (do not exceed 40°C). Tests are supplied with at least 6
months shelf life.
Safety
The Pocket Diagnostic test device contains no hazardous materials to humans, animals, plants or crops. The
accompanying extraction buffer contains a very small amount of sodium azide (0.05%) as a preservative – avoid
ingestion and skin contact. Refer to your government guidelines for the disposal of sodium azide.
Disposal of used tests
In cases where positive or suspect positive results all kit components should be regarded as contaminated and
should be disposed of appropriately. Contact the Food and Environment Research Agency (FERA) for further details
on how to do this. If you are not based in the UK please contact your government plant pathology and plant pathogen
quarantine department.
Test Procedure
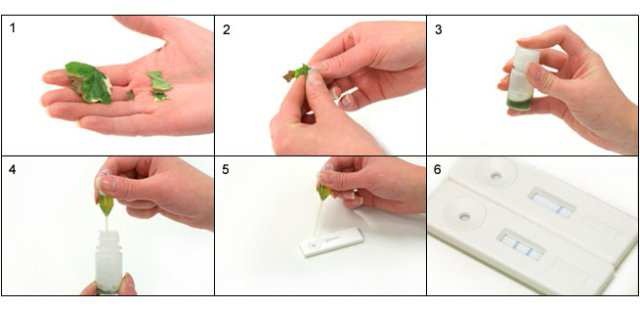
1. Select sample. Where possible select a part of the plant where diseased and healthy material meet, do not use
dead material. Use approximately 25mm square of material (See picture 1). Take care to avoid cross
contamination between samples from hands or cutting tools.
2. Cut or tear sample into small pieces and put into bottle.
3. Shake firmly for 30 seconds (longer for more resistant samples)
4. Wait 30 seconds allow the solution to settle and draw liquid into pipette avoiding too much plant material.
5. Add 2-3 drops into sample well of test strip.
6. Read result after 5-10 minutes.
Interpreting results
A line present next to the T (test line) indicates a positive result.
If the C line (control) does not appear the test has failed and must be repeated.
Ignore any changes to the result which occur after the 10 minutes has elapsed.
Literature
1. On-Site Detection of Plant Pathogens Using Lateral-Flow Devices. (C. Danks and I. Barker. 2000 OEPP/EPPO, Bulletin
OEPP/EPPO Bulletin30, 421-426)
2. Development of Potato Virus On-Site Test kits for Use by Plant Health Seed Inspectorate PHSI (Danks C and Barker I. Central
Science Laboratory, Sand Hutton, York, UK).
3. Development of a Field Test Kit for the Detection of Rhizomania in Sugar Beet Crops (Danks C, Shepherd V & Henry C. Central
Science Laboratory, Sand Hutton, York, UK).






